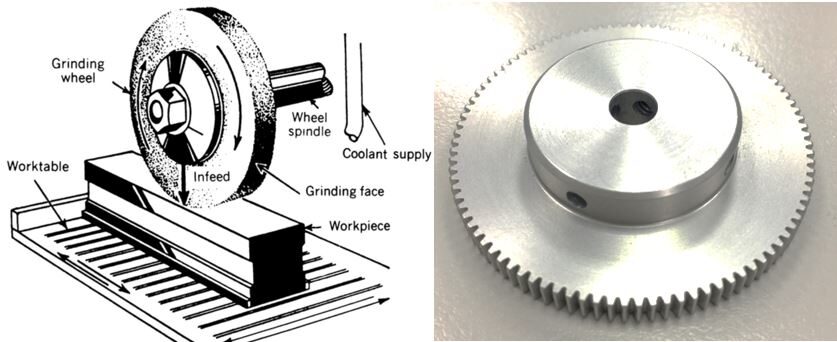
Image Source:https://engineerharry.wordpress.com/2012/04/21/grinding-machines-and-equipment/
In metal machining, grinding processes are crucial for precise surface finishes and meeting final application requirements. Here are some common design needs that require grinding process:
Surface Roughness Improvement: Grinding is employed when the surface roughness of metal parts does not meet specifications or when a smoother finish is needed to enhance appearance and tactile feel.
Application: In the aerospace industry, turbine blades require precise surface finishes to optimize aerodynamics and reduce drag. Grinding operations are utilized to achieve the required surface smoothness within tight tolerances.
Dimensional and Geometric Accuracy: Grinding is crucial for adjusting the dimensions, shapes, and parallelism of parts to ensure compliance with design requirements. This is particularly critical for high-precision components such as mechanical parts and bearings.
Application: In automotive manufacturing, crankshafts demand high dimensional accuracy and surface finish to minimize friction and ensure smooth engine operation. Grinding processes are employed to achieve the precise geometry required for optimal performance.
Removal of Surface Defects: Metal machining processes can result in defects such as burrs, cracks, or oxide layers. Grinding effectively removes these defects, enhancing the quality and durability of the parts.
Application: In the medical device industry, surgical instruments require defect-free surfaces to prevent contamination and ensure sterilization. Grinding operations are used to eliminate any surface imperfections and ensure the safety and reliability of the instruments.
Enhancement of Surface Finish: Some applications necessitate highly polished surfaces, such as optical devices and reflective mirrors. Grinding is employed to achieve the desired surface finish and reduce surface roughness.
Application: In the semiconductor industry, silicon wafers require ultra-smooth surfaces to ensure precise photolithography processes. Grinding techniques are utilized to achieve sub-nanometer surface finishes essential for semiconductor manufacturing.
Provision of Specific Surface Textures: Certain designs require specific surface textures or patterns to improve friction, lubrication, or visual aesthetics. Grinding can achieve these requirements, such as polishing or sanding operations.
Application: In the automotive sector, gear teeth are ground with specific surface textures to enhance meshing performance and reduce noise. Grinding processes are employed to achieve the desired tooth profile and surface roughness for optimal gear operation.
Residual Stress Relief: Metal machining generates residual stresses that may affect part performance and stability. Grinding can alleviate or eliminate these residual stresses, enhancing part stability and longevity.
Application: In the manufacturing of aerospace components, such as aircraft landing gear, residual stresses induced during machining can compromise structural integrity. Grinding processes are utilized to relieve these stresses, ensuring the durability and safety of the components.
In conclusion, grinding is vital in metal machining, facilitating the fulfillment of diverse design needs and application requirements to improve part quality, precision, and performance.
Please visit our pages CNC Turning Parts、CNC Milling Parts、CNC Machined Parts