Surface Roughness Fabrication Methods

Reference website https://www.foen-group.com/uploads/%E5%9B%BE%E7%89%871.png
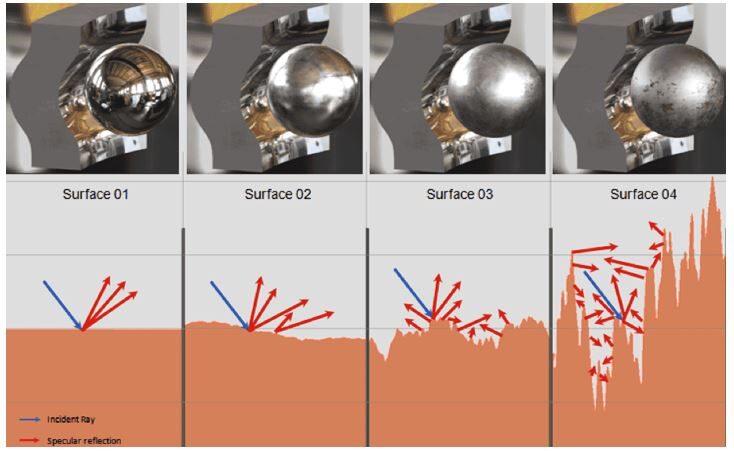
Шероховатость поверхности существенно влияет на различные механические свойства и функциональные возможности, такие как трение, износостойкость и уплотнительные возможности. Ниже приведены соответствующие фрагменты информации относительно достижимых методов изготовления:
Методы изготовления
1. Механическая обработка:
Процессы механической обработки, такие как фрезерование, шлифование, расточка и полировка, могут в определенной степени контролировать шероховатость поверхности. Например, шлифование часто позволяет добиться более мелкой шероховатости поверхности.
2. Химическая обработка:
Некоторые методы химической обработки могут изменять структуру поверхности и химические свойства металлов, тем самым регулируя их шероховатость. Примерами являются травление кислотой, гальванопокрытие и химическая полировка.
3. Термическая обработка:
Управляя процессами нагрева и охлаждения металлов, можно изменять их зернистую структуру и свойства поверхности, тем самым влияя на шероховатость поверхности.
4. Отделка поверхности:
Сюда входят такие методы, как окраска, покраска, анодирование и т. д., которые не только изменяют внешний вид металлических поверхностей, но и позволяют регулировать шероховатость поверхности.
5. Технологии 3D-печати:
Различные технологии 3D-печати (например, селективная лазерная плавка, электронно-лучевая плавка и т. д.) могут контролировать шероховатость поверхности металлических деталей. Корректировка параметров печати и методов постобработки может обеспечить различные требования к шероховатости.
При изготовлении металлических деталей выбор наиболее подходящего метода изготовления для контроля шероховатости поверхности обычно основывается на конкретных требованиях к применению и соображениях стоимости.
Если для вашего изделия имеются требования к шероховатости поверхности, убедитесь, что характеристики шероховатости поверхности (Ra) включены в ваш чертеж.
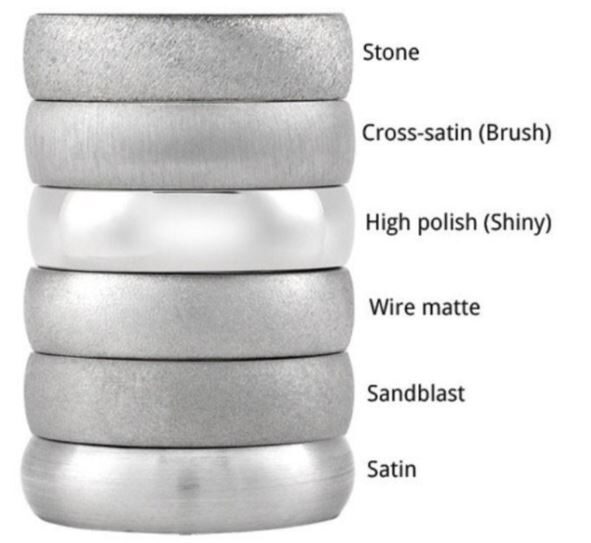
Reference website https://an-prototype.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Comparison-between-different-surface-roughnesses.png