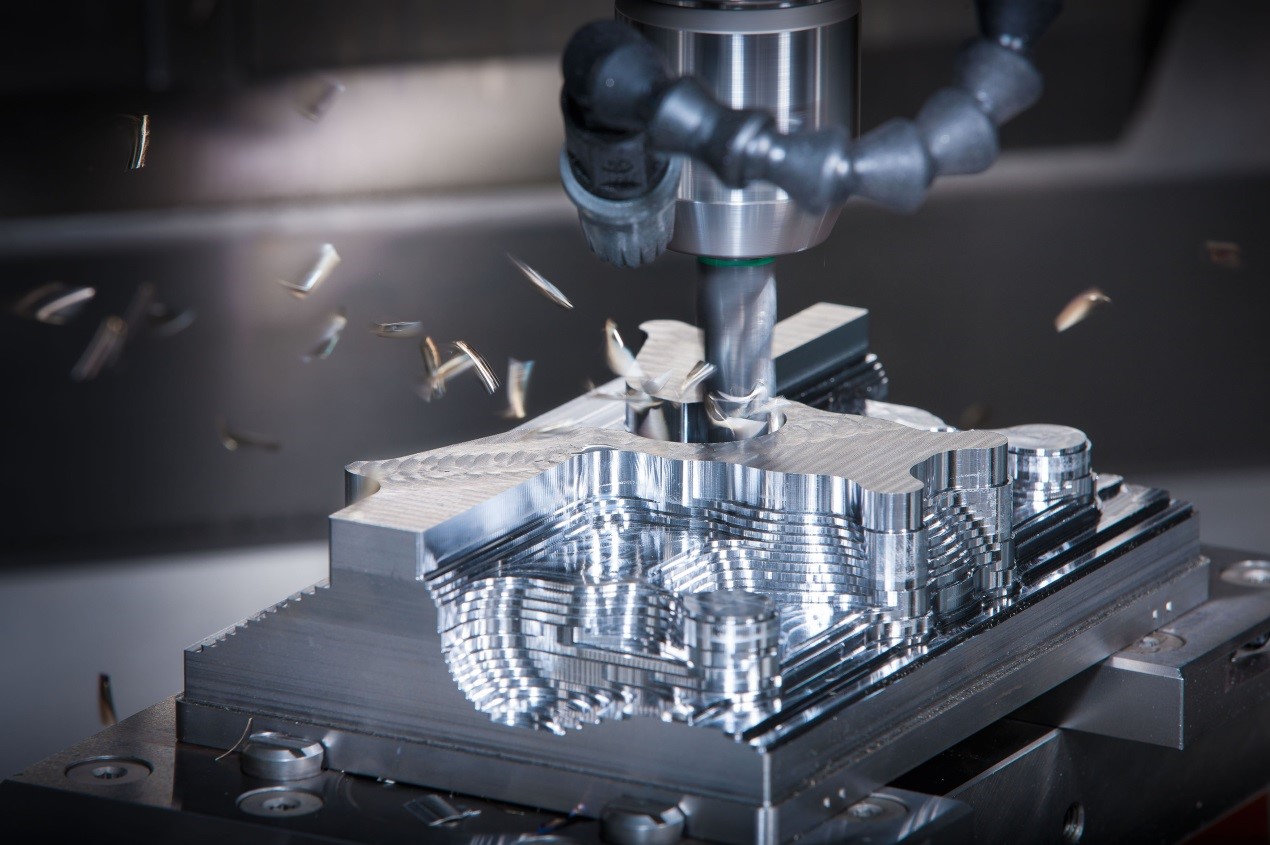
CNC Machining is a method of processing various workpieces with mechanical processing equipment. The main processing methods of mechanical processing are turning, drilling, boring, milling, planing, honing, super finishing and polishing.
The precision and surface roughness of machining can be processed in a wide range, and higher machining accuracy and very low surface roughness can be obtained.
These are the advantages of machining, so what else must you know about machining? What? The following Yuntuo Machining specifically introduces the machining knowledge that everyone wants to know.
Parts and functions of machining tools
The Role of Machining Geometric Plane
1. Cutting plane-a plane passing through any point on the main cutting edge and tangent to the machined surface.
2. Base plane————A plane that passes through any point on the main cutting edge and is perpendicular to the cutting speed direction, that is, perpendicular to the cutting plane.
3. The main section — the section that passes through any point on the main cutting edge and is perpendicular to the main cutting edge's projection on the base surface. Through the main section, the relationship between the front and base of the tool, the back and the cutting plane, the front and the back, the front and the cutting plane; the front angle, the main relief angle, the cutting angle, and the cutting angle can be determined.
4. Auxiliary cross-section --- the cross-section perpendicular to the projection of the auxiliary blade on the base surface; determine the auxiliary rake angle and auxiliary relief angle (radial)